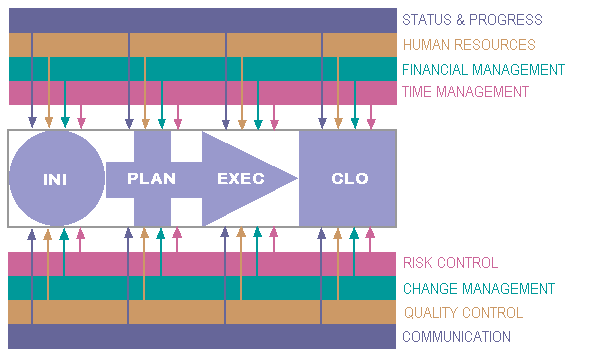
Project management processes |

|
During the project life cycle various project management processes impact on the phases. These processes are continuously monitored. |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
Risk control |
 |
Additional documentation |
| |
"Plan to avoid failure."
A risk: Any event which may probably happen and which can prevent the achievement of the project objectives and deliverables
Risk control: Systematic processes for the identification, analysis, monitoring and management of potential risks to prevent them from becoming a reality.
Issue: A risk that has been realised |
|
|
|
 |
 |
Time management |
 |
Additional documentation |
| |
TIME = MONEY
The project team’s time should be applied effectively. Keep track of the actual duration by means of time sheets.
Network diagrams and Gannt diagrams are two mechanisms that can be used to manage time.
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
Change management |
 |
Additional documentation |
| |
Change management: The process of leading and guiding human reaction to change. |
Change control: The formal process within a project to manage any change to the project. |
“If you allow the content of a project to change freely, the tempo of change will exceed the tempo of progress.”
|

|
Once the project plan and project documentation have been approved by the project board, the basis of the project is established ("baselined"). |

|
Implication: The project schedule, budget and scope are finalised and the project team is contracted to complete the plan. |

|
If any changes are required afterwards a formal process of change control is followed. |
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
Financial and cost management |
 |
Additional documentation |
| |
Financial management:
The processes required to ensure that the project is completed within the approved budget |

|
This involves the analysis of performance - among others planning, budget, implementation and control |
Cost management:
Accurate record-keeping of all financial transactions, payments, income, lists of debtors and creditors |
Please note that specific rules may apply in terms of certain initiatives or projects. |
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
Quality control |
 |
Additional documentation |
| |
"It costs less to do a task correctly the first time than to repeat the task."
Quality control: The processes required to ensure that the management of the project and the product or result that the project delivers meet the needs for which the project has been undertaken |
|
|
|
 |
 |
Human resources management |
 |
Additional documentation |
| |
The development of the team and stakeholders in order for them to function optimally as individuals as well as a team, and for them to make a contribution |
|
|
|
 |
 |
Communication management |
 |
Additional documentation |
| |
The processes required to ensure that appropriate project information is created, gathered and distributed at the right time |
|
|
|
 |
 |
Status reporting |
 |
Additional documentation |
| |
"That which is not on paper has not been said."
Status reporting: Regular reporting on various levels, for various roleplayers and according to pre-set standards
Guidelines are available on how to handle meetings, typical items on the agenda, status reports and decisions registers. |
|
|










